
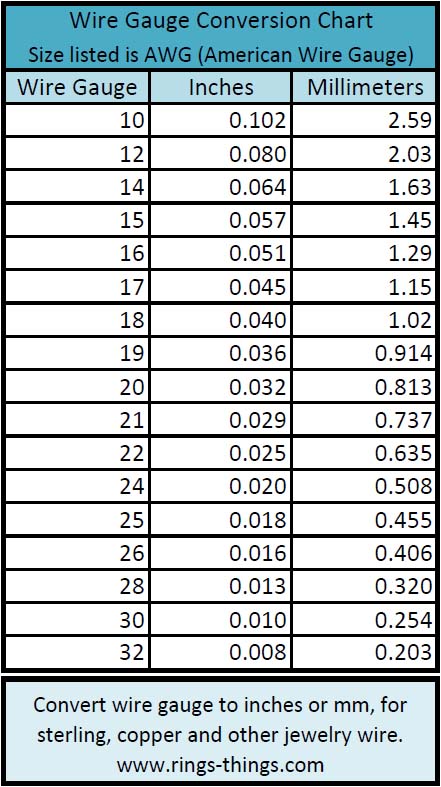
For example, AWG 4 has a resistance of 0.2485 ohms for 1000 feet, while AWG ohms resistance for 1000 feet at 25 degrees Celsius.Ĭurrent capacity (in amps): The current capacity is the amount of existing a wire can safely carry. If the two wires are of the same size, the thicker wire will have higher resistance than the thinner wire. The longer the wire, the higher the resistance. Resistance (Ohms/1000 feet): The wire’s electrical resistance depends on the thickness and the length. For example, AWG 40 needs 34.364 feet to get one pound of weight. As the Gauge descends three levels, the cross-sectional area doubles.įeet per pound: It means how many feet of wire you will need to reach the one pound of weight. Here r is the radius (half of the diameter) of the wire. The wire diameter doubles when the Gauge decreases by six levels, and it means a four-gauge wire will have double the diameter of a ten-gauge wire.Īrea: You can calculate the cross-sectional area of a wire with the formula A= πr2. For example, the diameter of AWG 4 is larger than the diameter of AWG 40. A small number means a large diameter, while a large number refers to a small diameter.

Thus, with the help of a wire’s Gauge, industries identify whether a wire is suitable for their application or not.ĭiameter: Wire gauges may vary from lower to higher numbers. The wire’s thickness affects its electrical properties. N= -39log 92 (R) + 36 Relationships Between Wire Gauge and Other Technical Specifications

Step 2– Now, you can use the following logarithm o calculate the American Wire Gauge number (n). Here, d (inch) is the diameter in inches, and d (mm) is measured in mm. The R is the ratio of wire’s diameter to that of standard Gauge (AWG#36) Step1– In this, you will calculate ratio R. To calculate the wire gauge with the help of diameter, you can use the following formula. Here n (from 36 to 0) is the AWG size, the value of n=-1 for Nr.00, n=-2 for AWG 000, n=-3 for AWG 0000. To calculate the diameter of an AWG wire, you can use the following formula.ĭ n =0.005inch*92 (36-n)/39 = 0.127mm*92 (36-n)/39 In contrast, the percentage of diameter for gauges two steps apart is (1.12293) ² ≈ 1.26098. so, for these two, the diameter ratio is 1.12293. Now suppose A and B are two successive gauges, and their diameters are dia A and dia B. As a result, the diameter increases with the falling gauge number. Now, as the gauge number decreases, the cross-sectional area increases. The ratio of these two diameters is 1.92. There are 40 gauges between these largest and smallest sizes, or you can say 39 steps. The diameters of these two are 0.005 inches and 0.46 inches, respectively. Image: different colored wires AWG FormulasĪccording to the American Wire Gauge (AWG) method, the highest Gauge of a wire is Nr. With this method, you can specify gauges for solid, nonferrous, and round electrically conductive wires. The AWG method is a standard method developed in the United States.
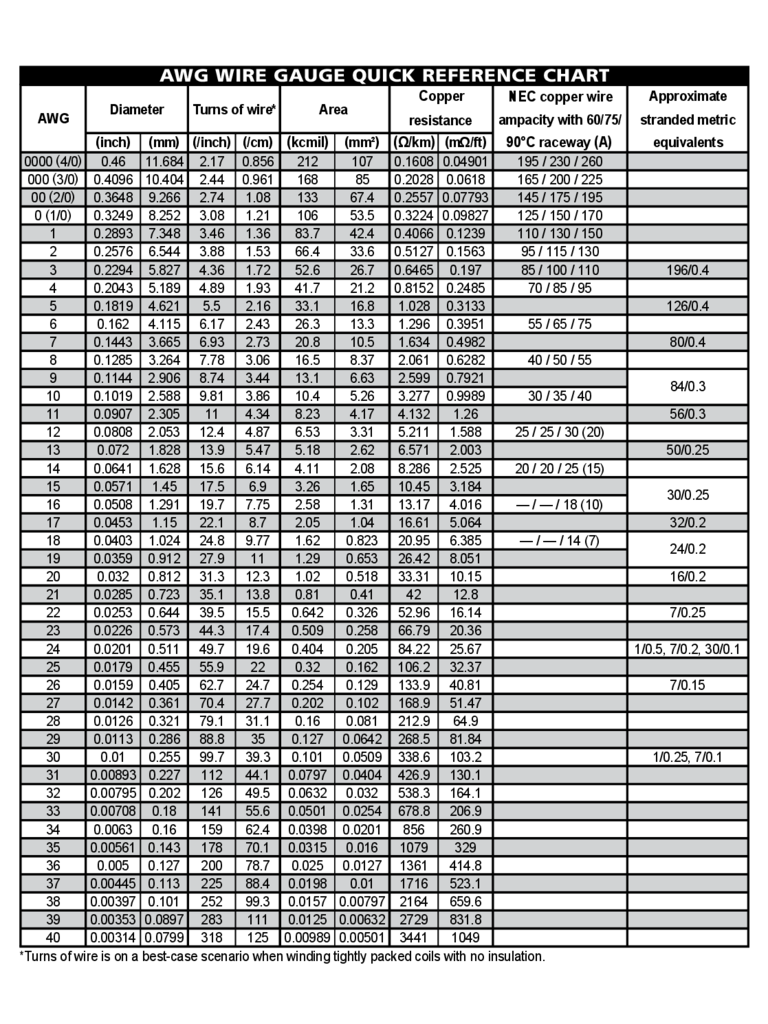
Industries use the American Wire Gauge method to measure the thickness of a wire. The higher the number, the thinner the wire is. The Gauge of an electrical wire means the thickness of the wire. Typical Applications of Standard Wire Gauges.Relationships Between Wire Gauge and Other Technical Specifications.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
